Definition of Terms
- Area – extent of part of a surface enclosed within a boundary.
- Calculation – the act or process of or result of calculating.
- Circumference – distance around the circle.
- Classification – group or category within an organized system.
- Decimal – number expressed in a counting system that uses units of 10, especially a decimal fraction.
- Dimension – measurable extent such as length, thickness and width.
- Fraction – number expressed as a quotient of two other numbers.
- Geometric Shapes – characterized by straight line, regular curves and angles.
- Graduation – scale of a measuring tool .
- Mensuration – act or art of measuring.
- Perimeter – bounding line or curve of a plain area.
- Standard – serves as a measure of reference.
- Stock – refers to a lumber for a certain furniture job.
- Substrate – wood to be cut in a cutting machine.
- Volume – space inside a solid figure.
|
Learning Outcome 1:
|
Select measuring equipment
|
Information Sheet 1.1
TYPES OF MEASURING TOOLS
HANDLING OF MEASURING INSTRUMENTS / TOOLS
A. DO’S
- Wipe measuring tools/instruments before returning them to the storage room.
- Oil the movable parts of the measuring tools such as zigzag rules, calipers, dividers and compasses to avoid stock-up.
- Make sure that grits like sand do not get inside the housing or case of a pull-push rule to avoid wearing off of the graduations.
- Check the lock of a pull-push rule if it is working.
B. DON’T’S
- Do not wipe off edges of the steel tape of pull-push rule with bare hands to avoid injury.
- Do not pull the steel tape of pull-push rule too much to avoid the coil spring from damage.
- Do not use the caliper as tongs.
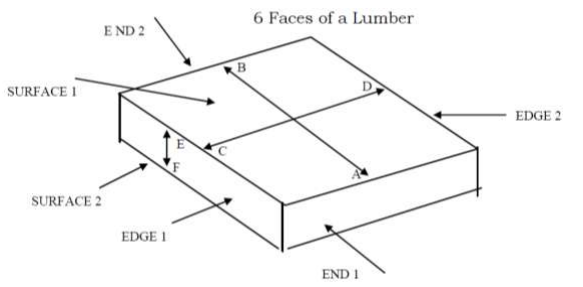
LINEAR MEASUREMENTS FOR THE 6 FACES OF LUMBER
|
Learning Outcome 2:
|
Carry out measurement and calculations
|
Information Sheet 2.1
SYSTEM OF MEASUREMENTS
The two (2) systems of measurements are: the English and the Metric System. The English system originated in England also known as the U.S. customary system of measurement while the Metric System was developed in France and also known as the S. I. (International Standard).
I. (UNIT OF MEASURES) - LINEAR MEASUREMENT
|
ENGLISH
Yard ( yd ) meter Foot ( ft ) / („ ) decimeter 1/10 |
METRIC
meter decimeter 1/10 meter centimeter 1/ 100 meter millimeter 1 /1000 meter |
II. READING OF MEASUREMENTS
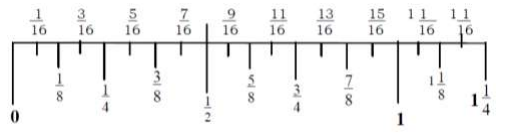
A. Reading the inch
The inch is divided into segments called graduations. Each graduation represents a measurement in form of a proper fraction. The inch can be divided into 16, 8, 4 and 2, equal parts.
The inch is divided into segments called graduations. Each graduation represents a measurement in form of a proper fraction. The inch can be divided into 16, 8, 4 and 2, equal parts.
Note: The illustration is not the actual lengh of an inch.
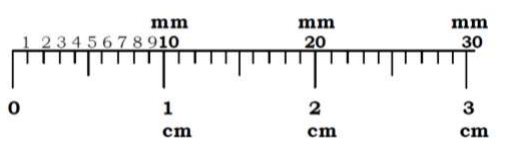
B. Reading the centimeter and milimeter
III. CONVERTING FRACTION TO DECIMAL
In converting fractions to decimals, divide the numerator by its denominator whether it is proper, improper or mixed fraction.
IV. CONVERTING UNITS OF MEASURE
V. TAKING DIMENSIONS
Ways of taking dimension
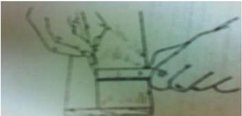
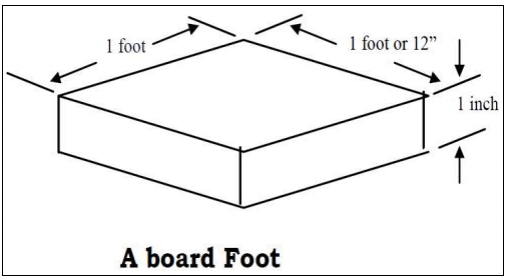
CALCULATING BOARDFOOT OF LUMBER
Although the International System (SI) or Metric System had already superseded the English System of measure, the board foot as a unit of measure for determining the volume of lumber is still being used by the furniture & cabinet maker and construction industry. This is because lumbers are sold in terms of board foot.
A board foot is actually one square foot of lumber of one inch thick
The formula used in computing board foot is:
Board foot (Bd. Ft.) = T x W x L 12
Where:
Note: This formula is being used for sawed wood of commercial dimension.
Board foot (Bd. Ft.) = T x W x L 12
Where:
- T = Thickness in inches
- W= Width in inches
- L = Length in feet
Note: This formula is being used for sawed wood of commercial dimension.
Example: Compute the board foot of lumber whose dimension is 2” x 4 “x 12”
Steps 1. Identify the given data
Given.
Find the Bd. Ft. = ?
Step 3. State the formula
Formula: Bd. Ft. = T x W x L
12
Step 4. Substitute the given data in the formula, then solve.
Solution:
Bd. Ft. = T x W x L
12
= 2” x 4” x 12 “ 12
= 96/12
= 8 Bd. Ft
Steps 1. Identify the given data
Given.
- T = 2”
- W = 4”
- L = 12‟
Find the Bd. Ft. = ?
Step 3. State the formula
Formula: Bd. Ft. = T x W x L
12
Step 4. Substitute the given data in the formula, then solve.
Solution:
Bd. Ft. = T x W x L
12
= 2” x 4” x 12 “ 12
= 96/12
= 8 Bd. Ft
Additional Information:
|
|
|